Causes, Symptoms, Physiotherapy Interventions, and Prognosis
source: lezdotechmed.com
Introduction
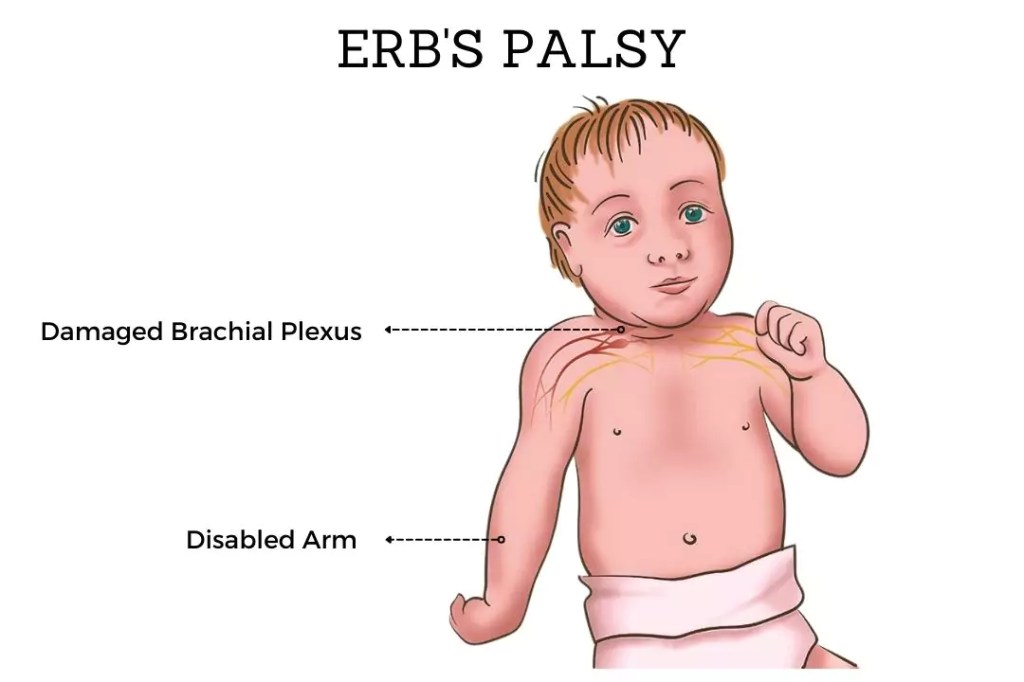
Erb’s Palsy, sometimes called brachial plexus birth palsy, is a disorder that develops when the brachial plexus nerves are injured during childbirth. This injury might cause paralysis or weakness in the afflicted arm, which can be difficult for the patient and call for a multimodal treatment plan that includes physiotherapy sessions. It usually results from a physical damage sustained during the delivery of the baby or from a severe force applied to the upper arm and shoulder. It can affect both adults and babies. The network of nerves known as the brachial plexus is located close to the neck and gives mobility and sensation to the shoulder, arm, hand, and fingers.
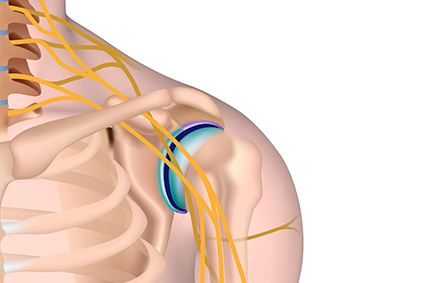
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that sends signals from the spinal cord to the shoulder, arm and hand. A brachial plexus injury occurs when these nerves are stretched, compressed, or in the most serious cases, ripped apart or torn away from the spinal cord.
Causes
The main cause of Erb’s Palsy is birth trauma, especially in cases when there are problems during delivery, such as shoulder dystocia, breech presentation, macrosomia, or maternal diabetes. When the baby’s shoulder gets stuck behind the mother’s pubic bone during birth, the brachial plexus nerves—which control arm movement and sensation—may be strained, compressed, or torn.
Symptoms
Characteristic symptoms of Erb’s Palsy include weakness or paralysis in the affected arm, manifesting as difficulty in moving or controlling muscles. Notably, there may be limited movement in the shoulder, arm, or hand on the affected side. Sensory abnormalities like numbness or tingling sensations may also occur. Diagnosis typically involves a comprehensive physical examination, medical history review, and sometimes imaging studies to assess the severity of nerve damage.
Physiotherapy Interventions
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in the management of Erb’s Palsy, aiming to improve muscle strength, range of motion, and functional abilities in the affected arm. Common physiotherapy interventions include:
- Range of Motion Exercises: Gentle stretching exercises are employed to improve flexibility and prevent joint stiffness. These exercises help maintain or restore the normal range of motion in the affected joints, facilitating functional movement.
- Strengthening Exercises: Specific exercises target weakened muscles to enhance strength and endurance. Progressive resistance training may be utilized to gradually build muscle mass and improve overall muscle function.
- Neuromuscular Reeducation: Therapeutic techniques such as proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) or sensory-motor training aim to enhance neuromuscular control and coordination. These approaches help individuals develop more efficient movement patterns and improve motor skills.
- Functional Training: Practical activities and functional tasks are incorporated into therapy sessions to simulate real-life situations. This approach helps individuals apply newly acquired skills to everyday activities such as self-care tasks, dressing, and household chores.
- Modalities: Therapeutic modalities such as electrical stimulation, ultrasound, or heat/cold therapy may be used adjunctively to relieve pain, reduce muscle spasms, and promote tissue healing.
Prognosis
The prognosis for Erb’s Palsy varies based on factors such as the extent of nerve injury, age at onset, and response to treatment. Physiotherapy, when initiated early and performed consistently, can significantly improve outcomes and functional independence. While some individuals may achieve full recovery or substantial improvement in arm function, others may experience residual weakness or limitations. Long-term follow-up and ongoing rehabilitation may be necessary to address evolving needs and optimize long-term outcomes.
Conclusion
Erb’s Palsy poses particular difficulties that need for an all-encompassing approach to treatment, with physical therapy being essential to recovery. Individuals with Erb’s Palsy can improve their functional abilities, muscle strength, and range of motion by putting customized physiotherapy therapies into practice. This will ultimately improve their quality of life and ability to participate in daily activities. To improve treatment methods and assist those impacted by this illness in their quest for empowerment and recovery, more study, outreach, and advocacy are crucial.