Comprehensive Guide to Managing Psoriatic Arthritis through Physiotherapy
Introduction
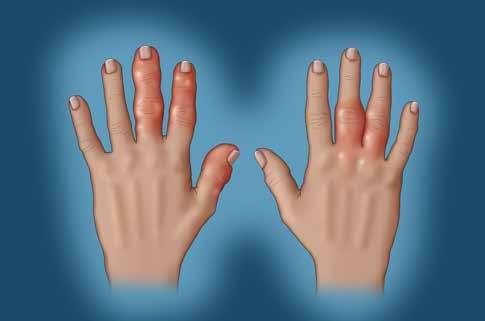
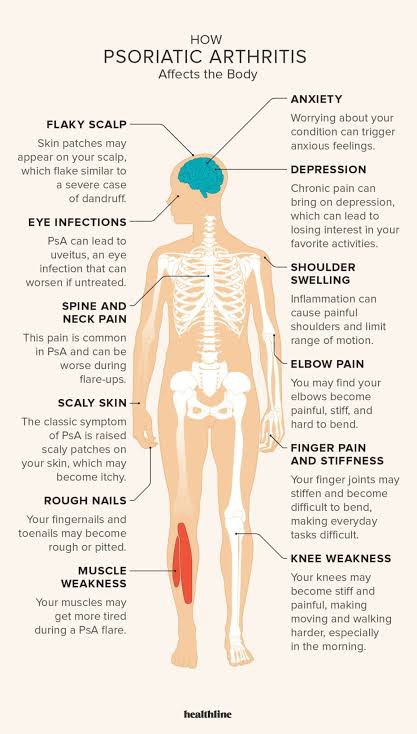
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects individuals with psoriasis, a skin disorder characterized by red, itchy, and scaly patches. This condition causes joint inflammation, leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling. However, physiotherapy interventions have proven effective in managing PsA symptoms, improving mobility, and enhancing overall quality of life.
Causes
The exact cause of psoriatic arthritis remains unclear, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. A family history of PsA or psoriasis increases the risk of developing the condition. Certain triggers such as infections, trauma, or stress may also contribute to its onset.
Epidemiology
Psoriatic arthritis affects approximately 30% of individuals who already have psoriasis, with symptoms often manifesting between the ages of 30 and 50. It affects both men and women equally, although studies have shown that men tend to develop more severe forms of the disease. PsA can significantly impact a person’s physical function, work productivity, and overall well-being.
Pathophysiology
Psoriatic arthritis is driven by an abnormal immune response known as autoimmune disorder. In individuals with PsA, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, including joints, leading to inflammation and tissue damage. This chronic inflammation can affect any joint in the body, commonly in the fingers, toes, knees, and spine.
Multidisciplinary Approach A multidisciplinary team approach to psoriatic arthritis involves bringing together a team of specialists to evaluate the condition and provide the best possible care. This team can include dermatologists, rheumatologists, psychiatrists, psychologists, physiotherapists, gastroenterologists, cardiologists, ophthalmologists, and endocrinologists. The collaboration between dermatologist and rheumatologist is crucial for the management of patients suffering from both psoriasis (PSO) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
This approach can help drive patient-centered care and encourage better adherence. Patient satisfaction has emerged as a central indicator of quality, and patient-centered care must remain a central goal for the care of patients with PsA.
Physiotherapy Interventions
- Exercise therapy:
Exercise plays a crucial role in managing PsA symptoms and promoting joint flexibility and strength. A physiotherapist can develop an individualized exercise program that includes range-of-motion exercises, stretching, and low-impact aerobic activities. Regular exercise helps reduce joint stiffness, alleviate pain, and prevent functional decline. - Manual therapy:
Physiotherapists skilled in manual therapy techniques can employ hands-on interventions to enhance joint mobility, decrease pain, and restore function. Techniques such as joint mobilization and soft tissue manipulation can loosen stiff joints, reduce muscle tightness, and improve overall movement. - Hydrotherapy:
Water-based exercises provide a low-impact environment for people with PsA to improve joint flexibility and muscular strength. Hydrotherapy sessions, conducted in a heated pool, can ease pain and inflammation, promoting relaxation and mobility. - Education and self-management:
Physiotherapists can educate individuals with PsA about the condition, its management, and self-care techniques. They can provide guidance on pacing activities, joint protection strategies, and the proper use of assistive devices. Empowering patients with knowledge helps them understand and manage their condition effectively. - Assistive devices:
Physiotherapists may recommend and prescribe assistive devices such as splints, braces, or crutches to support painful and inflamed joints. These devices can reduce stress on the affected joints, provide stability, and enhance function.

Conclusion
Psoriatic arthritis is a chronic inflammatory condition that can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life. However, with the help of physiotherapy interventions, individuals with PsA can effectively manage their symptoms, reduce pain, and improve joint mobility. A tailored physiotherapy treatment plan, including exercise therapy, manual therapy, hydrotherapy, education, and self-management strategies, can help individuals lead a more fulfilling and active life despite this challenging condition.
Source:
(1) Multidisciplinary Teams for Psoriatic Arthritis: On Aims and Approaches. https://www.actasdermo.org/es-multidisciplinary-teams-for-psoriatic-arthritis-articulo-S1578219014000766.
(2) Multidisciplinary Management of Psoriatic Arthritis: The Benefits of a …. https://www.academia.edu/97268989/Multidisciplinary_Management_of_Psoriatic_Arthritis_The_Benefits_of_a_Comprehensive_Approach.
(3) Multidisciplinary Management of Psoriatic Arthritis: The Benefits of a …. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12325-019-00901-0.
(4) Multidisciplinary Management of Psoriatic Arthritis: The Benefits of a …. https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s12325-019-00901-0.pdf.
(5) Our Multidisciplinary Approach – Psoriasis Center – Dermatology …. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/dermatology/specialty/psoriasis/multidisciplinary-approach.aspx.